Table of Contents
FAIR data
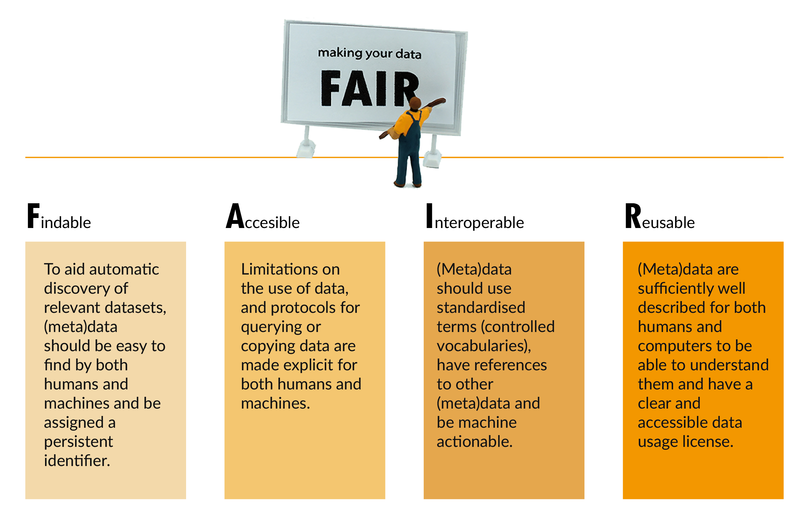
The attention of researchers is increasingly directed to the phases of the research lifecycle in which data are published, shared, discovered and reused. One of the perceived ways to achieve optimal reuse is to make data FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable) (Force 11, 2014; Wilkinson, et al., 2016).
The FAIR guiding principles consist of 15 facets (GO FAIR, n.d.) which describe a continuum of increasing reusability. Importantly, data should not only be FAIR for humans but also for machines, allowing, for instance, automated search and access to data. Funders like the European Commission have drafted Guidelines on FAIR Data Management for the H2020 programme (European Commission, 2016). Good data management is one way to support the FAIR principles.
Steps toward FAIRer data
In this guide, we treat the FAIR principles as guidelines to a clear higher goal: the aim is to prepare your research data for optimal (re-)use from the beginning and take appropriate measures that are most likely to be successful. To achieve FAIRness, data objects should at least have:
- A persistent identifier (PID) for the data object as a whole
Persistent identifiers like DOIs prevent link rot. Link rot is the process by which hyperlinks stop referring to the original source through time because they are moved or deleted. Without a PID, the data object simply will not be findable let alone reusable in the long-run (see 'Data citation'). - A sufficient set of metadata
A sufficient and standardised set of metadata (elements which describe the data) will enhance findability, interoperability, and reusability. The quality of the descriptive information regarding the data has a profound impact on their reusability. So the more documentation of the data’s context, the better. As a minimum, there should be sufficient amount of metadata to make the data findable but also understandable and reusable by other researchers (see 'Documentation and metadata'). - A clear licence
Researchers (and computers) who find a dataset should immediately know what they are allowed to do with it. Stating clear re-use rights is like having a warm 'Welcome' on the doormat of your dataset. The motto is: ‘open if possible, restricted if necessary’ (see 'Data licensing').
One of the ways to make sure your data will not become useless in the long-run is to choose a (trusted) data repository which has these attributes built into its infrastructure for dataset submission. It is the interest of FAIR data that researchers deposit their data, along with all the documentation needed for their understanding and re-use, in a (trusted) research data archive that has an explicit goal of data preservation and the necessary expertise to store data sustainably and maintain their usability (Van Berchum & Grootveld, 2017).
Making data FAIR is a joint responsibility of researchers and data repositories. In a comprehensive document, the Swiss National Science Foundation explains (SNF, n.d.) how the responsibilities of both are distinct.
In the chapter on archiving and publishing data, we will guide you in making the FAIRest choice for entrusting your data.
Take the Data Steward Moodle Course developed by FAIRSFAIR in conjunction with EOSC Synergy to learn more about FAIR.
Watch this video to discover more on FAIR:
Please cite this video as: CESSDA Training Team. (2020). Make Your Research Data F.A.I.R [Video]. Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4569345
Expert tip
- How FAIR are your data?
Want to know how FAIR your data are? Have a look at the checklist by Jones and Grootveld (2017). You can also use the FAIR-Aware tool (Akerman et al. 2021), a more detailed overview of the different aspects of FAIR when it comes to evaluating datasets